Cooling Machine For Cold Storage Supports Efficient Energy Use
 By Admin
By Admin
Cold storage facilities are essential for preserving perishable goods and maintaining consistent supply chains. In recent years, there has been an increasing focus on energy efficiency and sustainability in refrigeration systems. A cooling machine for cold storage plays a central role in this effort, combining reliable performance with thoughtful energy management. The integration of components such as a welded ball valve can significantly influence system efficiency, providing both operational stability and long-term reliability.

The Role of Cooling Machines in Energy Management
Cooling machines for cold storage operate continuously to maintain precise temperature levels. These systems must manage thermal loads efficiently, balancing energy consumption with cooling output. By optimizing how energy is distributed, cooling machines can reduce unnecessary power usage while ensuring that stored goods remain at stable temperatures. Modern designs focus on integrating energy-saving features, such as variable-speed compressors and intelligent controls, that respond to changing environmental conditions.
A cooling machine for cold storage is not only responsible for temperature control but also for supporting the overall energy strategy of a facility. For instance, the inclusion of a welded ball valve within the piping network ensures smooth fluid flow and less pressure drops. This type of valve can endure fluctuating temperatures and pressure changes without compromising performance, which contributes to maintaining steady energy consumption.
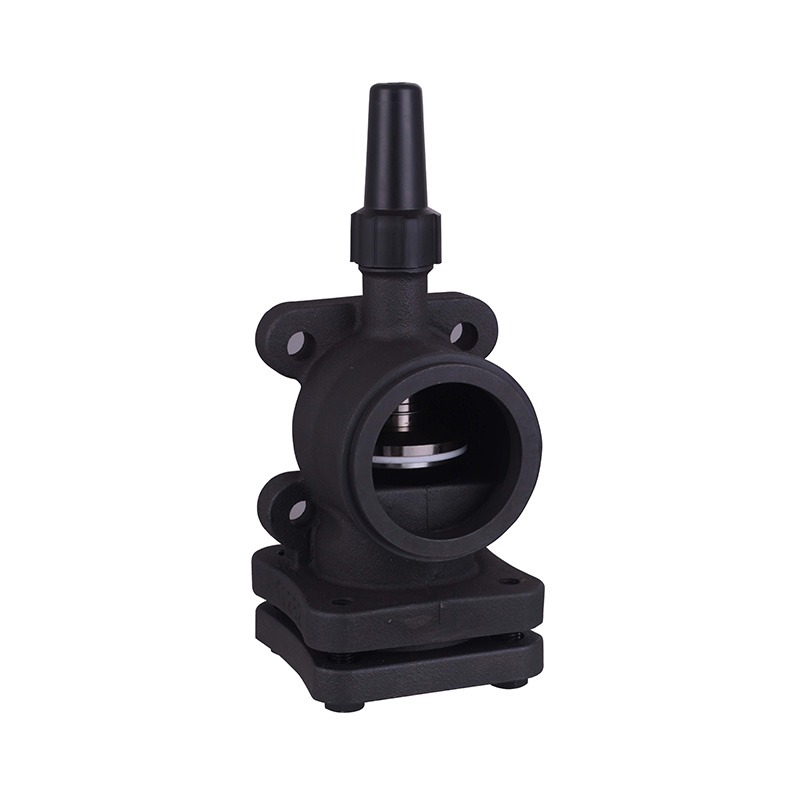
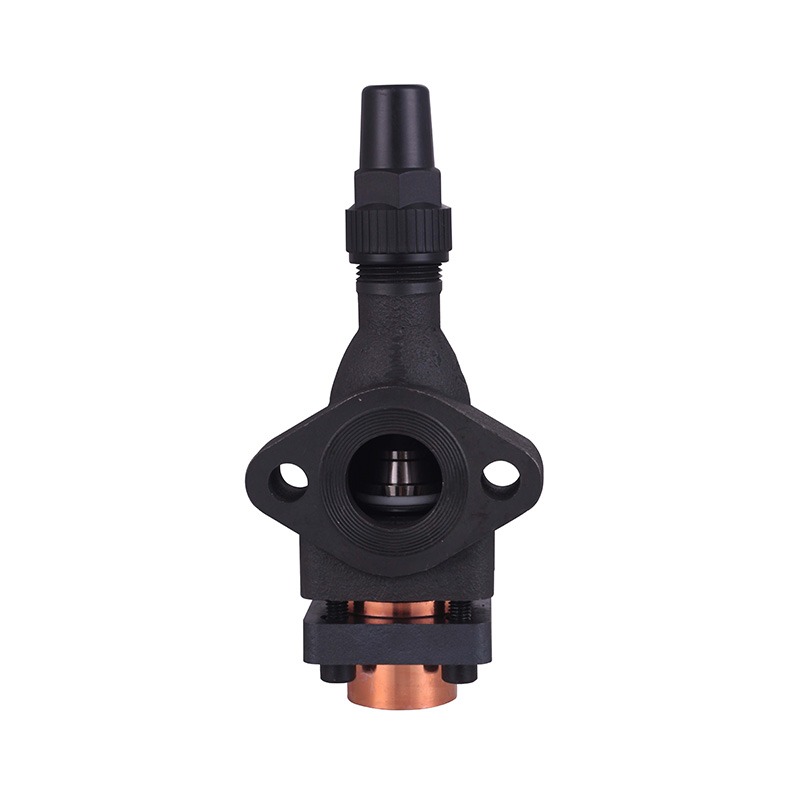
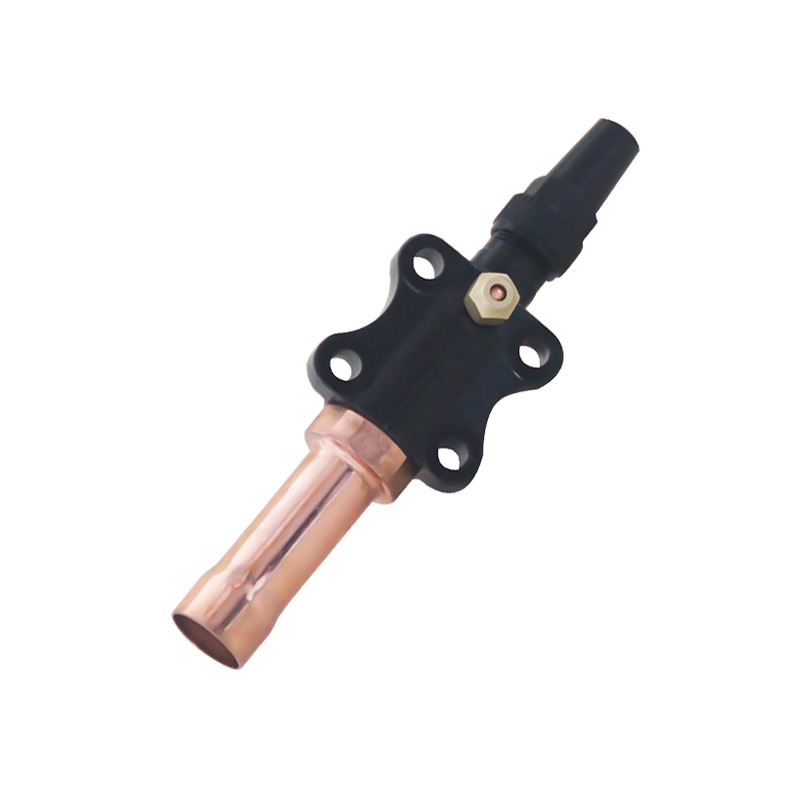
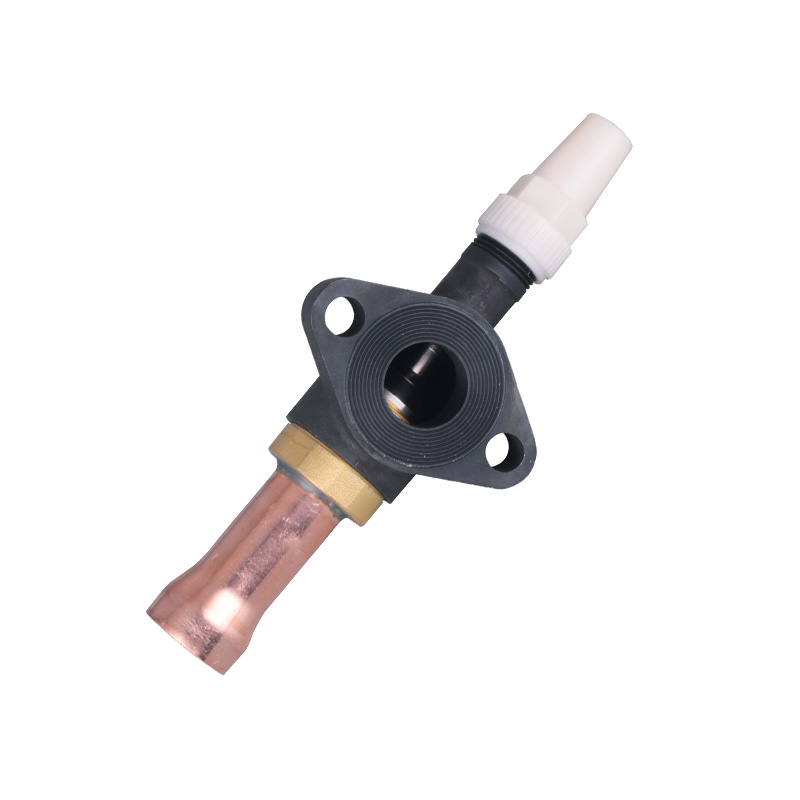
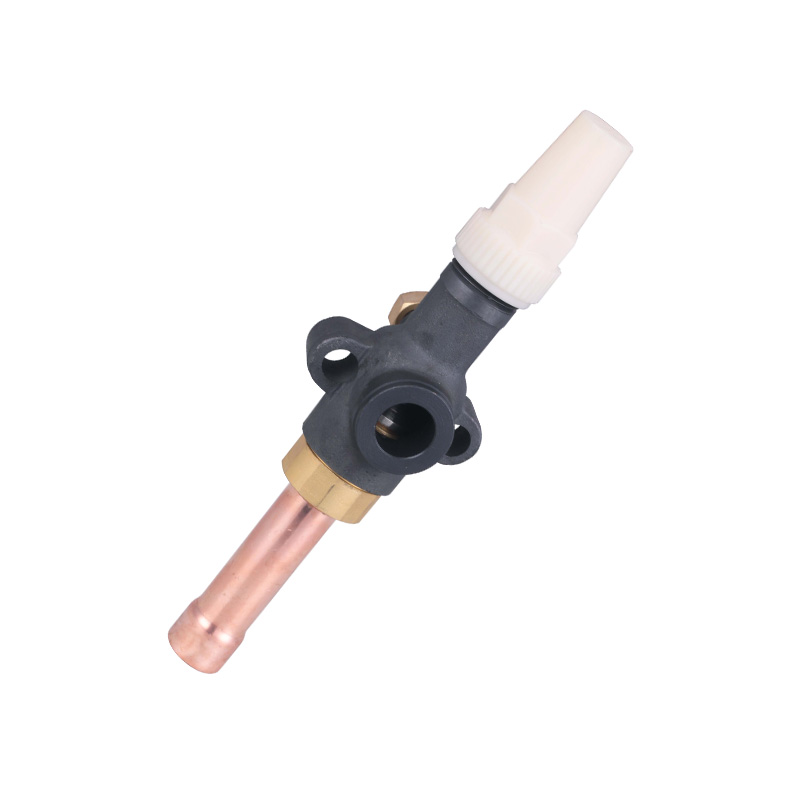
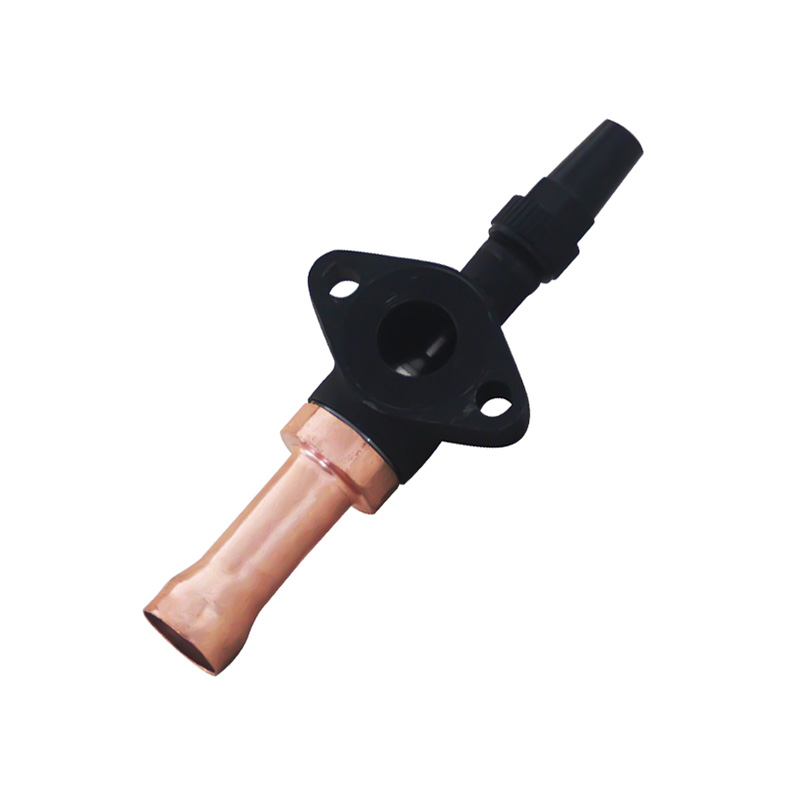
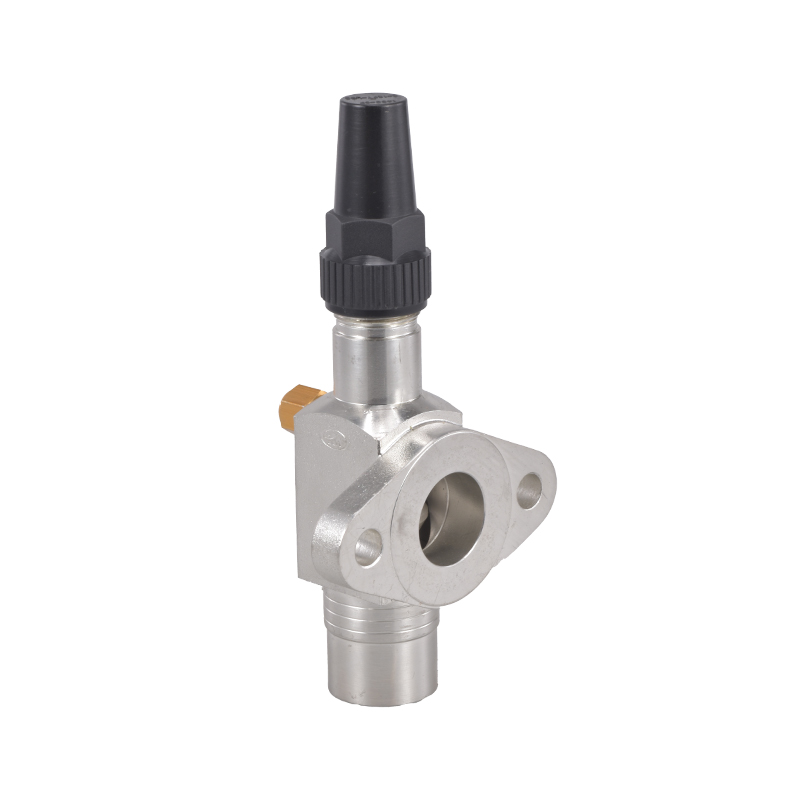
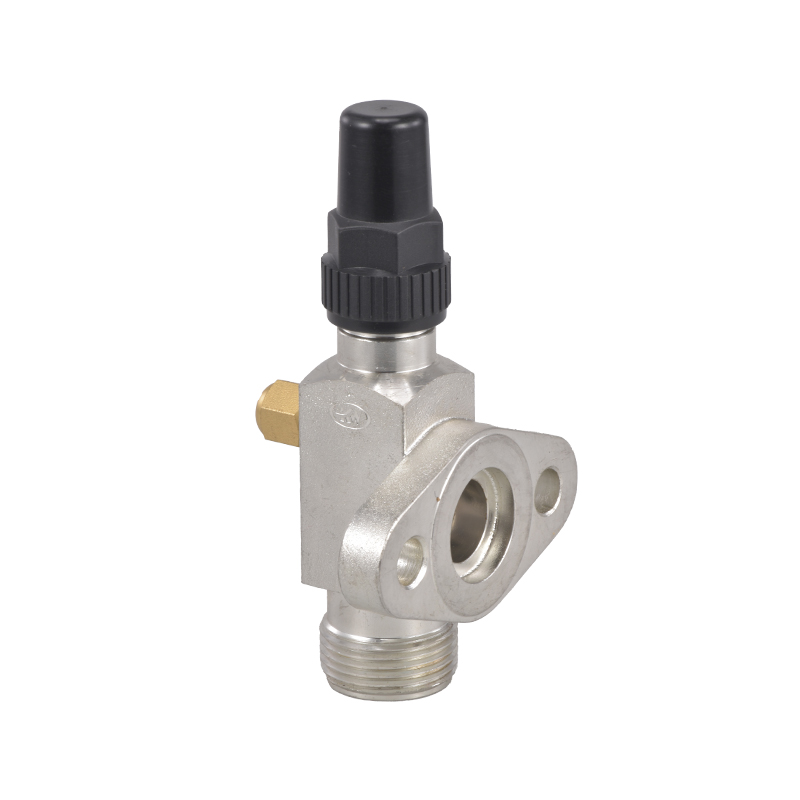
Welded Ball Valve: Reliability and Precision
The welded ball valve is a critical component in refrigeration pipelines. Its design allows for tight sealing and small leakage, which is vital for systems that handle refrigerants under pressure. In a cooling machine for cold storage, the presence of a welded ball valve ensures that refrigerant flows efficiently between compressors, evaporators, and condensers. By reducing the likelihood of leaks or flow restrictions, these valves help maintain consistent system performance and energy usage over time.
Furthermore, the durability of a welded ball valve reduces the need for frequent maintenance or replacements, indirectly supporting energy efficiency. Downtime for repairs can advance to temporary inefficiencies in temperature control, so a robust valve helps the system run smoothly while less operational interruptions.
Integration With Cold Storage Infrastructure
When a cooling machine for cold storage is installed, careful attention is given to how it interacts with the storage environment. Proper insulation, airflow management, and pipeline design all influence energy consumption. The welded ball valve contributes by providing reliable control over refrigerant distribution, allowing operators to adjust flows as needed without losing system stability.
Energy efficiency is not solely about reducing electricity use; it also involves maintaining consistent temperatures to prevent spoilage and waste. A cooling machine for cold storage equipped with a welded ball valve supports this goal by offering precise flow control and dependable sealing. Over time, this combination helps facilities manage both energy costs and storage quality effectively.
Future Trends in Cold Storage Cooling
Looking ahead, energy efficiency will remain a key priority for cold storage operations. Innovations in cooling machine designs, combined with durable components like welded ball valves, are likely to enhance system performance further. Advanced monitoring and control technologies can optimize energy usage dynamically, responding to real-time demand fluctuations while maintaining safe storage conditions.
A cooling machine for cold storage plays a pivotal role in supporting efficient energy use. The inclusion of a welded ball valve enhances system reliability, ensures precise refrigerant flow, and less unnecessary energy loss. By focusing on these elements, cold storage facilities can maintain consistent temperatures, reduce operational inefficiencies, and contribute to more sustainable refrigeration practices.



 English
English русский
русский Deutsch
Deutsch








